

Getty Pictures
DNS over HTTPS is a brand new protocol that protects domain-lookup visitors from eavesdropping and manipulation by malicious events. Reasonably than an end-user machine speaking with a DNS server over a plaintext channel—as DNS has accomplished for greater than three many years—DoH, as DNS over HTTPS is understood, encrypts requests and responses utilizing the identical encryption web sites depend on to ship and obtain HTTPS visitors.
Utilizing DoH or an identical protocol generally known as DoT—quick for DNS over TLS—is a no brainer in 2021, since DNS visitors will be each bit as delicate as another information despatched over the Web. On Thursday, nonetheless, the Nationwide Safety Company mentioned in some circumstances Fortune 500 firms, giant authorities companies, and different enterprise customers are higher off not utilizing it. The motive: the identical encryption that thwarts malicious third events can hamper engineers’ efforts to safe their networks.
“DoH gives the profit of encrypted DNS transactions, however it could actually additionally deliver points to enterprises, together with a false sense of safety, bypassing of DNS monitoring and protections, considerations for inner community configurations and data, and exploitation of upstream DNS visitors,” NSA officers wrote in revealed suggestions. “In some circumstances, particular person consumer functions might allow DoH utilizing exterior resolvers, inflicting some of these points robotically.”
DNS refresher
Extra in regards to the potential pitfalls of DoH later. First, a fast refresher on how the DNS—quick for area title system—works.
When individuals ship emails, browse a web site, or do absolutely anything else on the Web, their gadgets want a manner to translate a website title into the numerical IP deal with servers use to find different servers. For this, the gadgets ship a website lookup request to a DNS resolver, which is a server or group of servers that usually belong to the ISP, or enterprise group the person is related to.
If the DNS resolver already is aware of the IP deal with for the requested area, it should instantly ship it again to the tip person. If not, the resolver forwards the request to an exterior DNS server and waits for a response. As soon as the DNS resolver has the reply, it sends the corresponding IP deal with to the consumer machine.
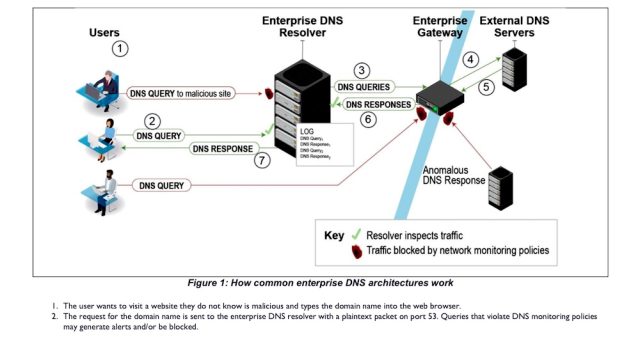
The picture beneath reveals a setup that’s typical in lots of enterprise networks:
NSA
Astonishingly, this course of is by default unencrypted. That implies that anybody who occurs to have the flexibility to monitor the connection between a company’s finish customers and the DNS resolver—say, a malicious insider or a hacker who already has a toehold within the community—can construct a complete log of each website and IP deal with these individuals join to. Extra worrying nonetheless, this malicious celebration may additionally have the opportunity to ship customers to malicious websites by changing a website’s right IP deal with with a malicious one.
A double-edged sword
DoH and DoT have been created to repair all of this. Simply as transport layer safety encryption authenticates Net visitors and hides it from prying eyes, DoH and DoT do the identical factor for DNS visitors. For now, DoH and DoT are add-on protections that require additional work on the half of finish customers of the directors who serve them.
The easiest method for individuals to get these protections now’s to configure their working system (as an example Home windows 10 or macOS), browser (corresponding to Firefox or Chrome), or one other app that helps both DoH or DoT.
Thursday’s suggestions from the NSA warn that these sorts of setups can put enterprises in danger—significantly when the safety entails DoH. The motive: device-enabled DoH bypasses community defenses corresponding to DNS inspection, which screens area lookups and IP deal with responses for indicators of malicious exercise. As an alternative of the visitors passing by the enterprise’s fortified DNS resolver, DoH configured on the end-user machine bundles the packets in an encrypted envelope and sends it to an off-premises DoH resolver.
NSA officers wrote:
Many organizations use enterprise DNS resolvers or particular exterior DNS suppliers as a key component within the total community safety structure. These protecting DNS providers might filter domains and IP addresses primarily based on recognized malicious domains, restricted content material classes, repute info, typosquatting protections, superior evaluation, DNS Safety Extensions (DNSSEC) validation, or different causes. When DoH is used with exterior DoH resolvers and the enterprise DNS service is bypassed, the group’s gadgets can lose these vital defenses. This additionally prevents local-level DNS caching and the efficiency enhancements it could actually deliver.
Malware also can leverage DoH to carry out DNS lookups that bypass enterprise DNS resolvers and community monitoring instruments, usually for command and management or exfiltration functions.
There are different dangers as nicely. As an example, when an end-user machine with DoH enabled tries to join to a website contained in the enterprise community, it should first ship a DNS question to the exterior DoH resolver. Even when the request finally fails over to the enterprise DNS resolver, it could actually nonetheless reveal inner community info within the course of. What’s extra, funneling lookups for inner domains to an out of doors resolver can create community efficiency issues.
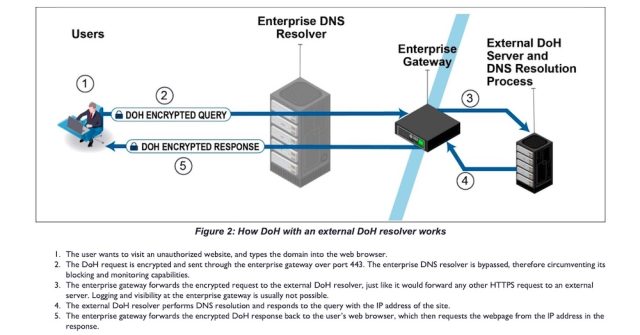
The picture instantly beneath reveals how DoH with an exterior resolver can utterly bypass the enterprise DNS resolver and the various safety defenses it could present.
NSA
Deliver your individual DoH
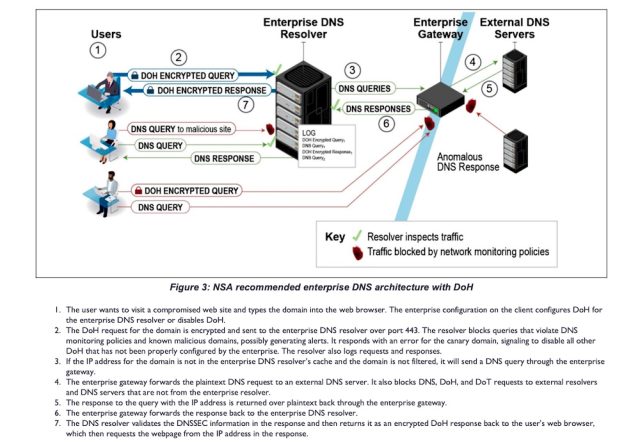
The reply, Thursday’s suggestions mentioned, are for enterprises wanting DoH to depend on their very own DoH-enabled resolvers, which in addition to decrypting the request and returning a solution additionally present inspection, logging, and different protections.
The suggestions go on to say that enterprises ought to configure community safety gadgets to block all recognized exterior DoH servers. Blocking outgoing DoT visitors is extra simple, because it all the time travels on port 853, which enterprises can block wholesale. That possibility isn’t accessible for curbing outgoing DoH visitors as a result of it makes use of port 443, which might’t be blocked.
The picture beneath reveals the really useful enterprise arrange.
NSA
DoH from exterior resolvers are nice for individuals connecting from dwelling or small workplaces, Thursday’s suggestions mentioned. I’d go a step additional and say that it’s nothing quick of loopy for individuals to use unencrypted DNS in 2021, after all of the revelations over the previous decade.
For enterprises, issues are extra nuanced.