
The sharp development in residential-broadband visitors seen in the course of the pandemic is beginning to degree off, new knowledge reveals. Whereas Web speeds have slowed considerably in lots of elements of the US, it seems that even rural-broadband networks are holding up fairly nicely.
Speeds have dropped in rural areas however are stabilizing, BroadbandNow reported immediately. Median obtain speeds in rural areas ranged from 16Mbps to 19.9Mbps in every of the primary 11 weeks of 2020. Speeds then fell to 15.5Mbps in March 22 to 28, the bottom recorded all 12 months. However rural speeds went again as much as 16.2Mbps within the week of March 29 to April 4.
Median add speeds in rural areas ranged from 5.5Mbps to six.3Mbps within the first 11 weeks of 2020 however have been simply 5.1Mbps the final two weeks, the identical report discovered:
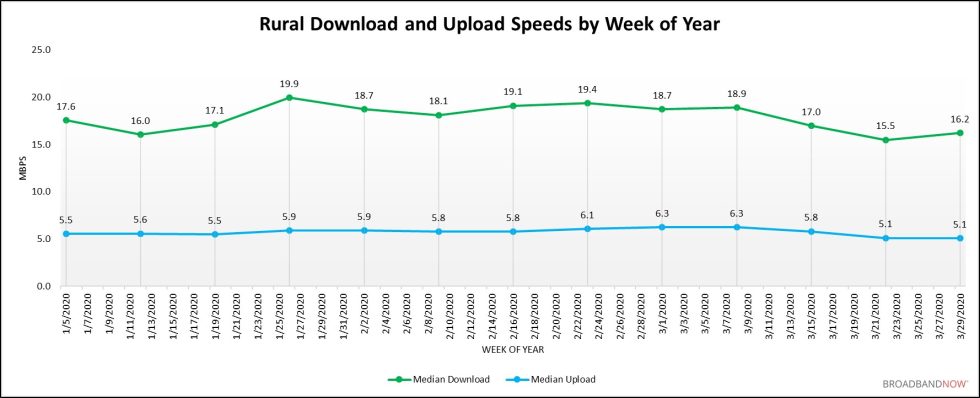
BroadbandNow
To find out rural efficiency, BroadbandNow stated it “aggregated speed-test outcomes [from M-Lab] throughout all US ZIP codes in counties marked as non-metropolitan (Micropolitan and Noncore) underneath the CDC’s City–Rural Classification Scheme.”
This is not a definitive measure of how rural-broadband networks are dealing with elevated residential utilization by individuals shedding jobs or working at house. For one factor, there’s “restricted availability of speed-test knowledge in rural communities,” BroadbandNow stated.
The group additionally hasn’t been in a position to present separate outcomes by know-how. DSL-only or satellite-only measurements would provide extra perception into broadband efficiency in areas with out fashionable networks like cable and fiber which have extra capability to deal with surges. Utilizing DSL or satellite tv for pc is usually a nasty expertise even in regular instances, and the networks are probably underneath extra pressure than traditional proper now.
Nonetheless, the BroadbandNow outcomes look like excellent news. Rural areas clearly have a better proportion of DSL and satellite tv for pc than city ones, and but median speed-test outcomes are stabilizing in each rural and concrete elements of the nation.
BroadbandNow is an organization that gives a web based device for checking broadband availability. Two weeks in the past, the corporate discovered that obtain speeds fell in 88 of the 200 most populous US cities, in comparison with the vary seen within the 10 weeks earlier than People began sheltering in place en masse. Even then, typical obtain speeds in huge cities remained excessive sufficient to assist regular broadband-usage patterns.
The variety of prime cities struggling decreases in median obtain speeds rose to 117 final week. However the BroadbandNow report launched immediately stated issues are turning round:
Web efficiency within the US improved general, with 97 cities (48.5 %) recording obtain velocity degradations this week (down from 117, or 59 % final week). 139 cities (69 %) have reported add velocity disruptions, which can be down from final week’s 144, or 72 %.
Downside areas embrace Baltimore, Maryland; Los Angeles, California; and Flushing, New York, the place add speeds had been greater than 40 % decrease than the vary seen within the 10 pre-pandemic weeks.
Trade knowledge reveals usage-growth slowing
Different knowledge additionally means that broadband-network utilization is hitting a plateau. Cable-industry foyer group NCTA stated yesterday that whereas peak downstream utilization is up 19 % since March 1, peak utilization truly went down about 1 % final week. “This might point out that shopper utilization and demand is leveling off, however we’ll need to see multiple week of information earlier than making any conclusions,” NCTA stated. (Peak utilization knowledge is a measure of the busiest instances of day.)
Peak upstream utilization continues to be rising, however the price of enhance is slowing. Peak add utilization has gone up 33 % since March 1, together with a 7.three % enhance between March 21 and 28. However the price of development slowed to 4.1 % within the week that ended April 4, the NCTA’s broadband-usage dashboard says. The dashboard is predicated on knowledge from Comcast, Constitution, Cox, and a number of other different cable firms.
Elevated use of video conferencing by individuals immediately working from house is probably going inflicting a part of the rise in upstream visitors. Cable networks usually provide a lot quicker obtain speeds than add speeds. NCTA stated that “Upstream peak hours in lots of areas have shifted from late night in the direction of afternoon.”
NCTA additionally stated that “spine networks have important capability and present no indicators of congestion.” This implies that any slowdowns seen by shoppers are extra probably brought on by congestion in last-mile networks that lead into individuals’s properties.
Will increase in residential-broadband utilization are apparently being matched by decreases in utilization at workplace buildings and different services. Throughout the pandemic, there’s been a 35 to 40 % drop in fiber-bandwidth utilization at companies, faculties, hospitals, authorities companies, and cell towers, based on commerce group Incompas.
There’ll at all times be occasional outages, and it could be tempting accountable them on pandemic-related congestion. However outages will also be brought on by mundane and simply fixable issues like a severed fiber cable. In the end, we might want extra intensive knowledge to find out how nicely broadband networks are holding up, significantly in areas that lack cable or fiber.
The FCC’s nine-year-old Measuring Broadband America program may assist on this regard, however the fee underneath Chairman Ajit Pai has not often offered up to date knowledge from the in-home exams carried out by this system. FCC Commissioner Jessica Rosenworcel, a Democrat on the Republican-majority company, has been pushing for the fee to analysis broadband efficiency and supply public updates each day. Pai hasn’t taken up her suggestion.
In a press release final week, Rosenworcel stated:
As extra People are informed to remain house, the FCC ought to research how broadband networks are faring underneath the stress of extra intensive use and publish these findings day by day… The adjustments in broadband consumption could reveal weak factors within the advanced ecosystem of firms, providers and merchandise that make up the Web. The FCC ought to use this chance to grasp how our networks are performing and keep forward of potential issues—as a result of if we look forward to these issues to be reported to us, it’s already too late.